| CAS
NO. |
28302-36-5 |
|
| EINECS
NO. |
248-950-7 |
| FORMULA |
C34H29CuN4O7·3Na |
| MOL
WT. |
C34H29CuN4O7·3Na |
|
H.S.
CODE
|
|
|
TOXICITY
|
|
| SYNONYMS |
|
| Trisodium
(2S-trans)-[18-carboxy-20-(carboxymethyl)-13-ethyl-12-formyl-2,3-dihydro- 3,7,17-trimethyl-8-vinyl-21H,23H-porphine-2-propionato(5-)-N21,N22,N23,N24]
Cuprate(3-); |
| SMILES |
|
|
CLASSIFICATION
|
|
|
GENERAL
DESCRIPTION OF CHLOROPHYLL & CHLOROPHYLLIN
|
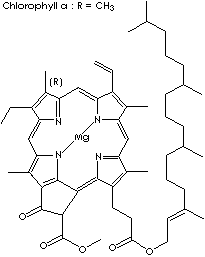
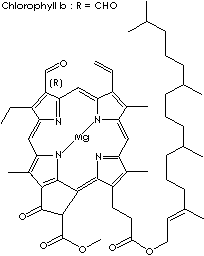
Chlorophyll is the generic name for several fat-soluble green plant pigments
which includes the open-chain bile pigments and the large ring compounds. The
structure of chlorophyll molecule has four nitrogen-containing pyrrole rings
bonded to a central magnesium atom, and the fifth ring containing only carbon
atoms, and various long hydrocarbon tails attached to the pyrrole rings. The
molecular structure of the chlorophylls is similar to that of the heme bound to
proteins forming hemoglobin, except that the latter contains iron(II) ion in the
center of the porphyrin. Chlorophyll a and b are the most common of the several
chlorophyll molecules. Chlorophylls a is a waxy blue-black microcrystalline
green-plant pigment, C55H72MgN4O5, with a characteristic blue-green alcohol
solution. Chlorophyll a occurs in all organisms exhibiting aerobic
photosynthesis (green plants, algae, and cyanobacteria). Chlorophyll b, occurs
in higher plants, is a similar green-plant pigment, C55H70MgN4O6, having a
brilliant green alcohol solution. There are chlorophylls c1 and c2 in diatoms
and brown algae, and chlorophyll d in red algae.
|
|
|
Chlorophyllin is a water-soluble salt obtained by alkaline hydrolysis of
chlorophyll with replacement of the magnesium by copper and methyl and phytyl
ester groups by sodium and potassium. Preparations of the salts are applied
topically for the deodorization of skin lesions and administered orally to
deodorize ulcerative skin lesions and the urine and feces in colostomy,
ileostomy, or incontinence. Chlorophyll absorbs visible radiation in the
blue-violet and red regions of the electromagnetic spectrum; the green portion
is not absorbed and transmitted and reflected, resulting in the green color
appearance of plant leaves. Chlorophyll plays an important role in the
conversion of sunlight into chemical energy in the process of photosynthesis.
In this biochemical process, the energy absorbed by chlorophyll transforms
carbon dioxide obtained from air and water absorbed by the roots into plant
food, carbohydrates and waste product of oxygen which, however, is released into
the environment for most life. The other plant pigments involved in light
harvesting and energy transfer in photosynthesis are carotenoids, phycobilin, or
phycoerythrin which become apparent when the amount of chlorophyll decreases and
show the other colors. |
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
green to black
powder |
| MELTING POINT |
|
| BOLING
POINT |
|
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
|
| SOLUBILITY
IN WATER |
Insoluble
|
|
SOLVENT
SOLUBILITY
|
soluble
in organic solvents including ether, benzene, white oil
|
| pH |
9.5
- 10.5 |
| VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
REFRACTIVE
INDEX
|
|
| AUTOIGNITION |
|
| NFPA RATINGS |
|
| FLASH
POINT |
|
| STABILITY |
Stable under ordinary conditions |
|
APPLICATIONS |
|
The intense color of chlorophyll is useful as a commercial pigment. It is used
as a green dye for food, toothpaste, detergents and cosmetics. It has chelating
agent activity also. It is
used in ointment, pharmaceutical (especially liver recovery and ulcer
treatment). It is applicable in luminescence chemistry, spectrophotometric analysis
as well as organic synthesis and polymerization catalyst. |
| SALES SPECIFICATION |
|
APPEARANCE |
green to black powder |
|
COLOR VALUE |
568 min (1% / 1cm 405nm) |
|
EXTRACTION RATIO |
3.0 - 3.9 max (E405nm/E630nm) |
| Cu CONTENT |
5.0% min |
|
Na CONTENT |
5 - 7.0% |
|
As |
2 ppm amx |
|
HEAVY METALS |
5 ppm max |
|
RESIDUE ON IGNITION |
30.0% min |
|
LOSS ON DRYING |
5.0% max
|
| TRANSPORTATION |
| PACKING |
25kgs in fiber drum
|
| HAZARD CLASS |
|
| UN NO. |
|
| OTHER INFORMATION |
|
Hazard
Symbols: n/a, Risk Phrases: n/a, Safety Phrases: 22-24/25 |

